

– Diffuse lupus nephritis (class IV):is the most common and severe form of lupus nephritis. There is also often extracapillary proliferation associated with focal necrosis and crescent formationĬlass III, Segmental endocapillary proliferation with karryorhextic debri and leukocyte infiltration –PASM Affected glomeruli may exhibit swelling and proliferation of endothelial and mesangial cells associated with leukocyte accumulation, capillary necrosis, and hyaline thrombi. The lesions may be segmental (affecting only a portion of the glomerulus) or global (involving the entire glomerulus).
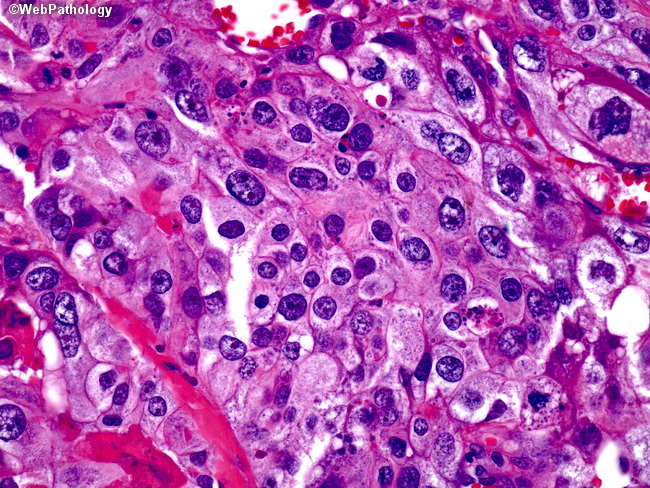
– Focal lupus nephritis (class III): is defined by involvement of fewer than 50% of all glomeruli. – Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis (class II):is characterized by mesangial cell proliferation, often accompanied by accumulation of mesangial matrix, and granular mesangial deposits of immunoglobulin and complement without involvement of glomerular capillaries. identified by immunoflourescence and byĮlectron microscopy, but without structural changes by light microscopy. – Minimal mesangial lupus nephritis (class I): is very uncommon, and is characterized by immune complex deposition in the mesangium. Lupus nephritis – six patterns have been recognized MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES INVOLVING VARIOUS ORGANS IN SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Positive LE cell is more specific for SLE and can found in 5 percent of rheumatoid arthritis, some scleroderma patients and in some drug induced reactionsĭisadvantages – Time consuming and usually false negative in immune-compromised individualsĪNTINUCLEAR ANTIBODIES STAINING BY IMMUNOFLOURESENCE TECHNIQUE:Ĭommercially available fluorescent tagged antibodies are used and the following patterns are demonstrated Īnemia – hemolytic blood picture on peripheral smear This is found in 50 to 80 percent of SLE patients The hemoxylin bodies are phagocytized by remaining viable leukocytes in a complement-dependent reaction resulting in blood granulocytes with cytoplasm stretched and nucleus by a homogenous inclusion which is stained blue by Leishman’s/Wright’s stainĪ LE cell test is considered positive when atleast four typical L.E. When these nuclei interact with antinucleoprotein antibodies in the serum, they are altered, with loss of chromatin pattern and a resultant homogenous appearance (hematoxylin bodies) Procedure – Heparinized blood is agitated with glass beads or by other mechanical methods so that nuclei are released from disrupted leukocytes. L E cell is an invitro phenomenon, rarely found in-vivo except in bone marrow or in inflammatory exudates Antibodies to non-histone proteins bound to RNA.The hallmark of SLE is the production of autoantibodies against nuclear and few cytoplasmic components that are neither organ or species specific LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS :


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
